- All
- Product Name
- Product Keyword
- Product Model
- Product Summary
- Product Description
- Multi Field Search

loading
Goldsite
GP33020
| Package size: | |
|---|---|
| Availability: | |
1. Intended Use
This product is used on GPP-100 Specific Protein Analyzer for quantitative determination of Complement 4 (C4) in human serum or plasma as an aid in diagnosis of abnormal C4 metabolism.
2. Summary
The complement system can be activated via the classical and the alternative pathways. C4 participates in activation in the classical pathway. A decrease in C4 is common, but complete absence is rare. A lowered concentration or the complete absence of C4 occurs in immunocomplex diseases, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), autoimmune thyroiditis and juvenile dermatomyositis. The commencement of SLE in patients with C4 deficiencies can often be detected at a very early stage, and the course of the disease is milder than in patients with normal complement levels. Infections such as bacterial and viral meningitis, streptococcal and staphylococcal sepsis and pneumonia are reported to be associated with decreased C4.
Additional differentiation can be obtained by the determination of C4 when the level of C3 is low. If in such cases the concentration of C4 is normal, then an activation of the alternative pathway is likely. The main use of C4 determinations is in assessing the course of hypocomplement conditions. As an acute phase protein, C4 is produced to an increased extent during inflammatory processes. It is elevated in systemic infections, noninfectious chronic inflammatory conditions (primarily chronic polyarthritis) and physiological states (pregnancy). The elevation rarely exceeds twice the normal value and can mask a reduction in the current consumption.
1. Intended Use
This product is used on GPP-100 Specific Protein Analyzer for quantitative determination of Complement 4 (C4) in human serum or plasma as an aid in diagnosis of abnormal C4 metabolism.
2. Summary
The complement system can be activated via the classical and the alternative pathways. C4 participates in activation in the classical pathway. A decrease in C4 is common, but complete absence is rare. A lowered concentration or the complete absence of C4 occurs in immunocomplex diseases, Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), autoimmune thyroiditis and juvenile dermatomyositis. The commencement of SLE in patients with C4 deficiencies can often be detected at a very early stage, and the course of the disease is milder than in patients with normal complement levels. Infections such as bacterial and viral meningitis, streptococcal and staphylococcal sepsis and pneumonia are reported to be associated with decreased C4.
Additional differentiation can be obtained by the determination of C4 when the level of C3 is low. If in such cases the concentration of C4 is normal, then an activation of the alternative pathway is likely. The main use of C4 determinations is in assessing the course of hypocomplement conditions. As an acute phase protein, C4 is produced to an increased extent during inflammatory processes. It is elevated in systemic infections, noninfectious chronic inflammatory conditions (primarily chronic polyarthritis) and physiological states (pregnancy). The elevation rarely exceeds twice the normal value and can mask a reduction in the current consumption.
Classical Immunoassay Technology: Nephelometry
All-in-one cartridge for single test
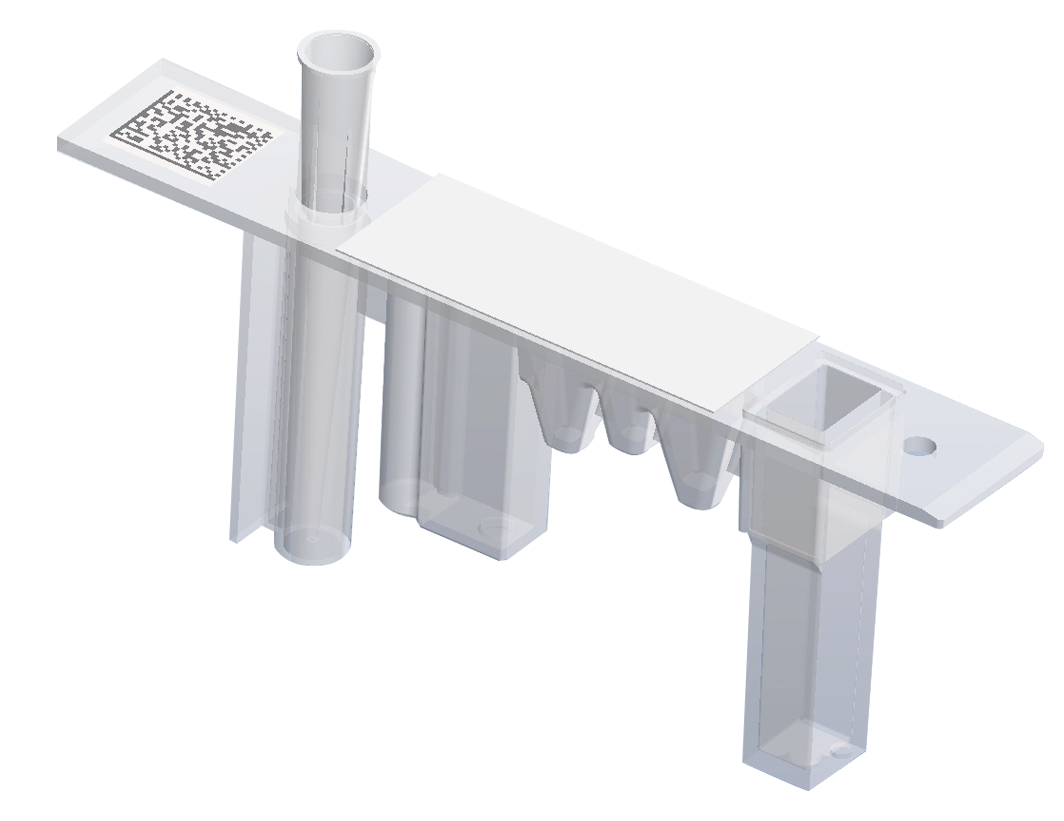

Classical Immunoassay Technology: Nephelometry
All-in-one cartridge for single test

The Most Innovative fully automatic Nephelometry analyzer
GPP-100
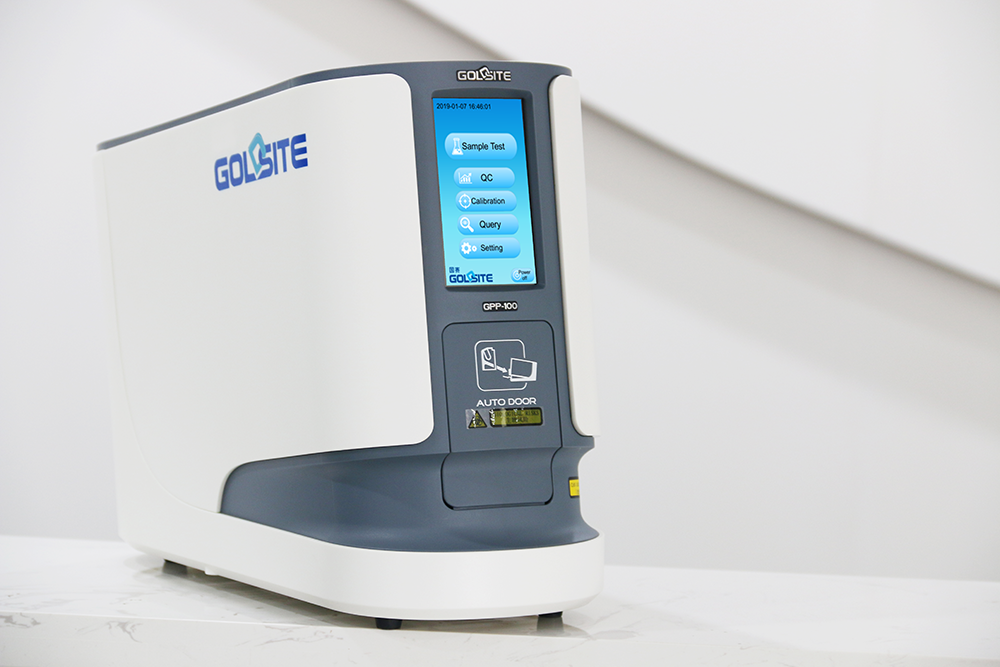

The Most Innovative fully automatic Nephelometry analyzer
GPP-100

We offer